Understanding Conditional Syntax
Conditions are special statements that you can use to limit the amount of data processed by a specific program. This topic describes the syntax for conditional statements and illustrates some examples for your reference.
Conditional syntax is similar to Boolean syntax, which allows you to enter selection criteria such as equal, less than, and greater than. You might be familiar with Boolean syntax if you have constructed an advanced search while using an Internet search engine such as Google.
Directions:
A conditional statement consists of three elements - a field name, an operator, and a comparison value.
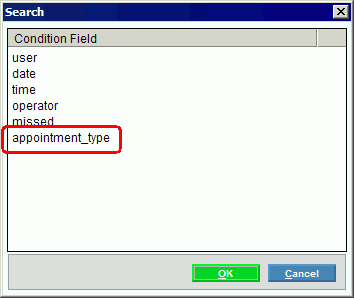
Field names must be entered exactly as expected by a program. For example, if the field name is appointment_type (with an underscore), then the program will not accept appointment type (with a space). Usually, the program provides a list of the eligible field names. See the examples later in this topic for more information.
Operators indicate how to evaluate the value for the specified field. The following operators are available.
|
Comparison Operators |
|
|
Operator |
Description |
|
= |
Equals |
|
!= |
Not Equal |
|
> |
Greater Than |
|
< |
Less Than |
|
>= |
Greater Than or Equal To |
|
<= |
Less Than or Equal To |
|
Other Operators Tip: For more information about the following operators, contact NDS Technical Support. |
|
|
Operator |
Description |
|
@SUB |
Substring (value, start position, end position) |
|
@FORMAT |
Format String (value, format) |
|
@UNFORMAT |
Unformat String (value, unformat) |
|
@ZEROFILL |
Zero-fill String (value, size) |
|
@COMBINE |
Concatenate Strings (delimited fields) |
|
@LENG |
Length of String (value) |
Comparison values are either numeric or alphanumeric values used as the criteria for selecting records. The following rules apply to entering comparison values:
You do
not have to leave any blanks between the field name, operator, and value.
(Surrounding
the operator with spaces is optional.)
Example: CURRENT=57.61
Negative
numeric values must be preceded by a dash (negative sign).
Example: CURRENT=-4.00
You must
surround alphanumeric values with double quotes.
Example: appointment_type
= "OV"
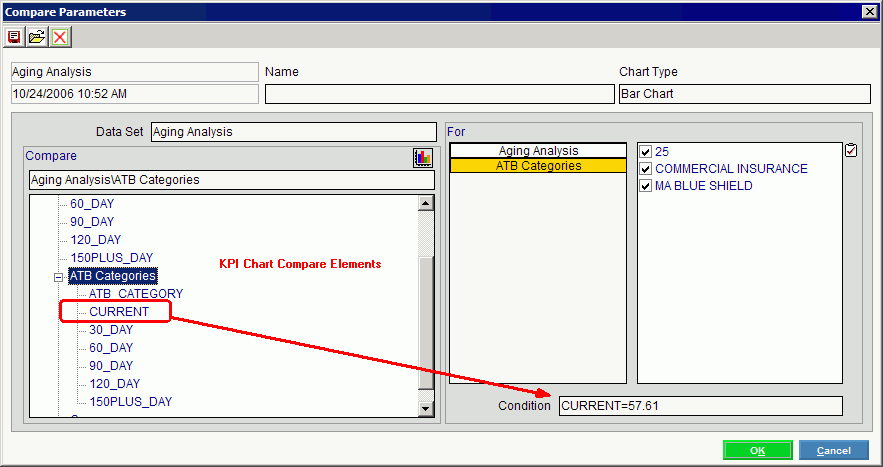
In the Executive Management System, you can enter a conditional statement for a chart view at the Compare Parameters Window of the Executive Console. In the following example, the fields that are eligible for conditional statements are listed under the KPI Chart Compare Elements. In this case, the field name is CURRENT. The operator is = (equals). And the comparison value is 57.61. The resulting compare view chart will only include ATB Categories whose values in the CURRENT field are equal to 57.61.
Executive Console - Compare Parameters Window Example

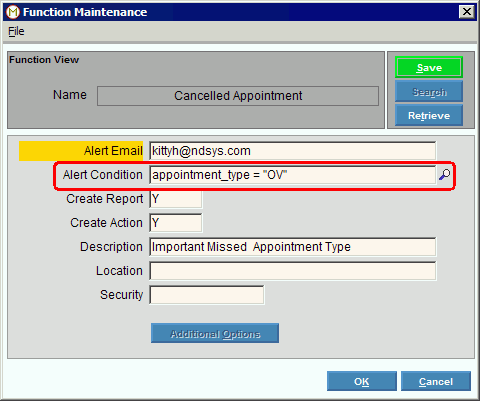
In other applications, you can set up alerts with specific conditions. In the following example, an alert email will be sent to the specified employee if an office visit (OV) appointment is cancelled. In this case, the field name is appointment_type. The operator is = (equals). And the comparison value is "OV".
Tip: Remember to surround alphanumeric values with double quotes.
Function Maintenance Window Example
Note: In
Function Maintenance, you can load an eligible field name from the Search
window. To
see a list of the eligible fields, click the Search ![]() icon.
icon.
Search for Eligible Fields Window Example