Standard Notation Rules, click More.
The following rules apply to the standard notation used for describing keyboard shortcuts that appear in WebHelp®.
-
Keyboard shortcuts are delimited by brackets [ ].
-
Names of special keyboard keys appear in bold capital letters.
Examples: [ALT], [CTRL] -
Names of keys for letters on the keyboard appear bold and lower case.
Examples: [f], [x] -
Keys separated by a plus sign must be pressed together. Press and hold the first key, then press the key following the plus sign.
Example: [CTRL + x] -
Keys separated by brackets [ ] must be pressed sequentially, without holding any other key during the sequence.
Example: [ALT] [f] [x]
Example: File Menu - Exit Command, click More.
Menus use keyboard shortcuts extensively. The following instructions describe how to exit from the module by using the keyboard shortcut [ALT] [f] [x].
-
Press the [ALT] key. You will then see an underscored letter in each menu name.
Example: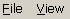
-
Press [f], which is the underscored shortcut that opens the File menu. You will then see the drop-down menu.
Example: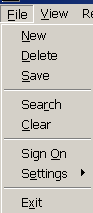
-
Press [x], which is the underscored shortcut that performs the Exit command.